Publications
Group highlights
(For full list of publications and patents see Google Scholar)
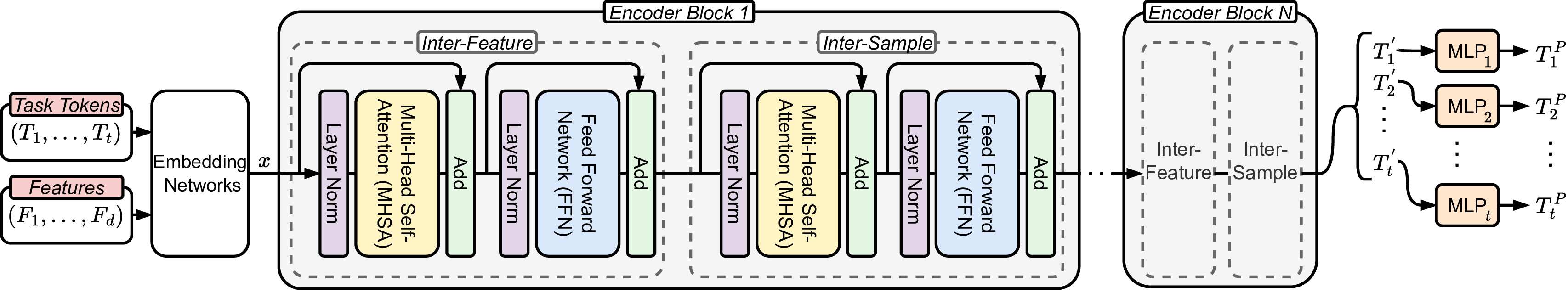
A framework for multitask learning on large tabular data, comprising MultiTab-Net, a transformer-based architecture that models feature dependencies while mitigating task competition, and MultiTab-Bench, a synthetic multitask generator for systematically evaluating multitask dynamics.
D Sinodinos, J Wei, N Armanfard
The 40th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI 2026)
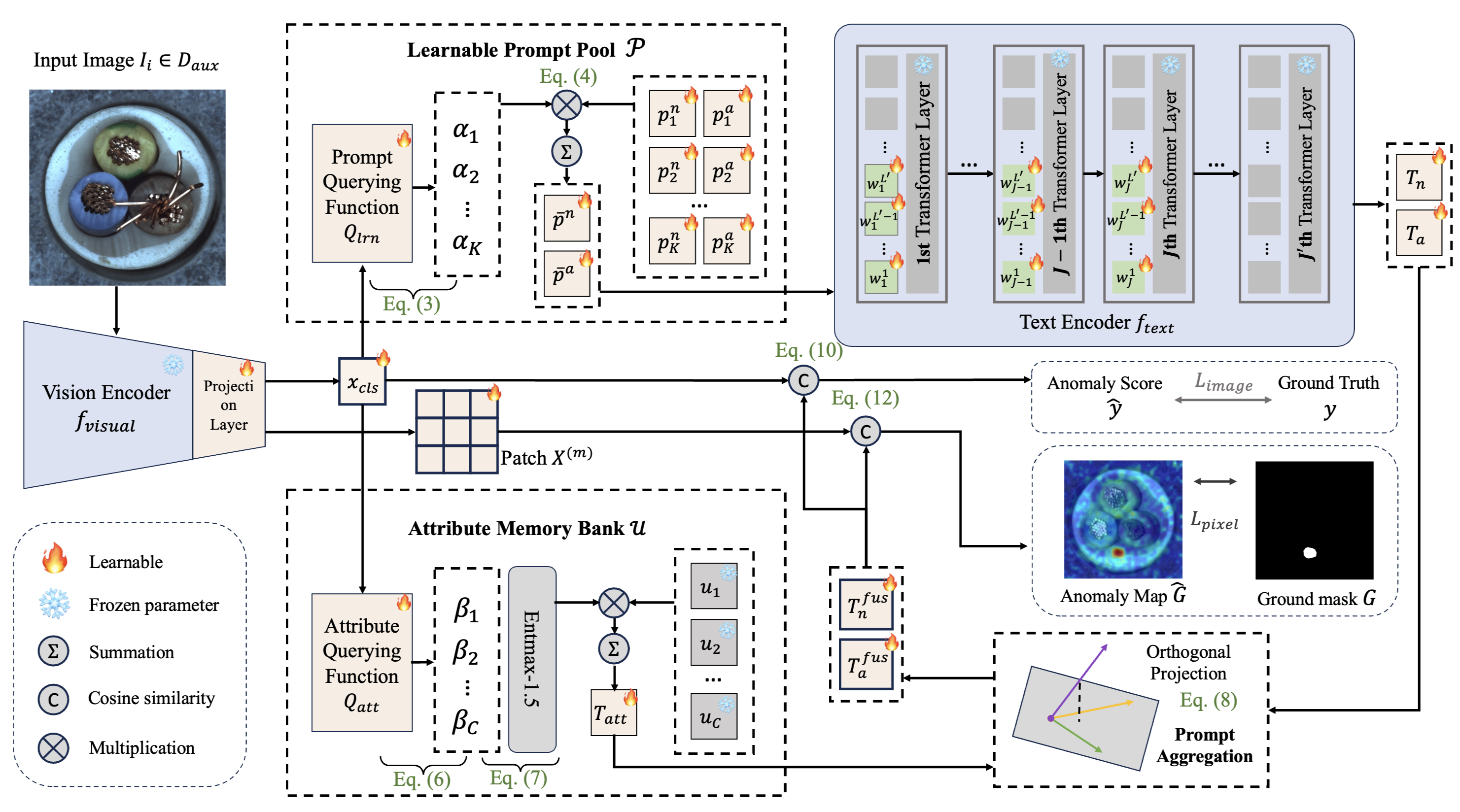
A framework integrating dual-branch prompt learning with label-free test-time adaptation for anomaly detection, using semantic cues to weight prompts and refining them via high-confidence pseudo-labels from unlabeled data.
Z Wang, S Kahou, N Armanfard
The 36th British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC 2025)

In this paper, we introduce LaHA, a novel framework that leverages language-guided deep reinforcement learning to identify and utilize informative data regions, thereby improving both interpretability and performance.
B Nikpour, N Armanfard
The 36th British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC 2025)

In this paper, we introduce a novel and practical end-to-end unsupervised time-series anomaly detection when the training data are contaminated with anomalies.
TKK Ho, N Armanfard
The 41st Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence (UAI 2025)

In this survey, we conduct a comprehensive and up-to-date review of Graph-based Time-series Anomaly Detection (G-TSAD)
TKK Ho, A Karami, N Armanfard
IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (IEEE TPAMI 2025)

This paper proposes Cross-Task Affinity Learning (CTAL), a lightweight module that enhances multitask networks by modeling local and long-range cross-task interactions via optimized task affinity matrices.
D Sinodinos, N Armanfard
IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV 2025 – Oral)

This paper introduces a novel, practical, and lightweight framework, namely the Graph-Jigsaw Conditioned Diffusion Model for Skeleton-based Video Anomaly Detection.
A Karami, TK Ho, N Armanfard
IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV 2025)

In this paper, we propose a novel deep clustering framework with self-supervision using pairwise data similarities (DCSS). We propose to form hypersphere-like groups of similar data points, i.e., one hypersphere per cluster.
M Sadeghi, S. Soleimani, N Armanfard

In this paper, we propose the first-ever algorithm to tackle the open-set multivariate time series anomaly detection problem, in which a few labeled samples from a limited class of anomalies are available during the training phase.
T Lai, TKK Ho, N Armanfard
27TH European Conference on Artificial Intelligence (ECAI 2024, Oral)
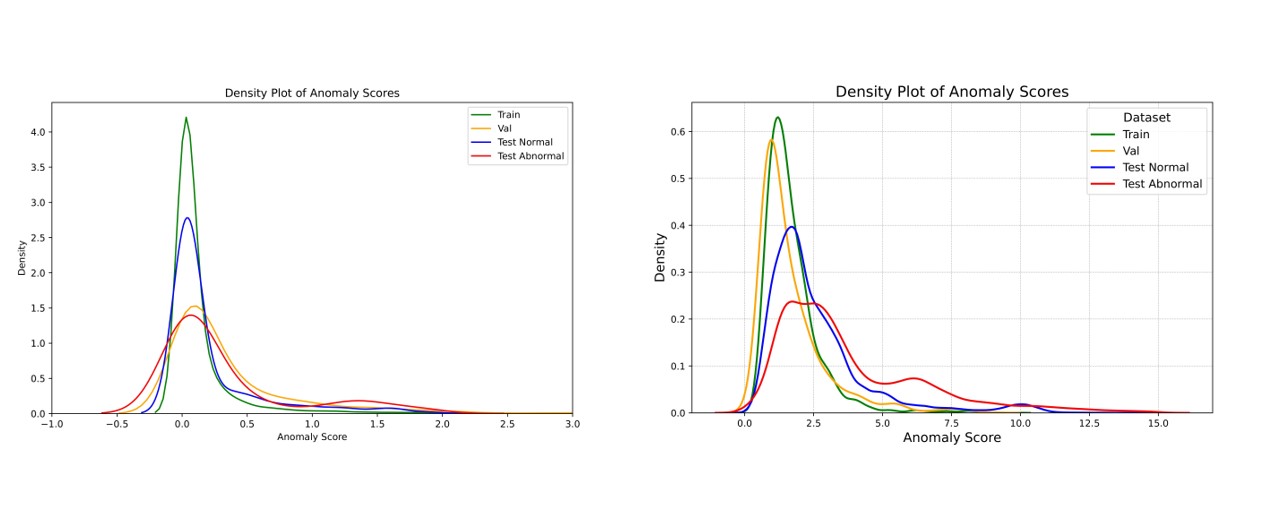
This paper provides a critical analysis of the initialization effects on TSAD model performance. Our extensive experiments reveal that TSAD models are highly sensitive to hyperparameters such as window size, seed number, and normalization.
A Koran, H Hojjati, N Armanfard
The 40th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence-ASTAD W

There is a noticeable lack of algorithms specifically designed for unsupervised clustering. To fill this gap, we introduce the concept of UCC in this paper.
M Sadeghi, Z Wang, N Armanfard

To facilitate further research in DRL-based human activity recognition, we have constructed a comprehensive survey on activity recognition methods that incorporate deep reinforcement learning.
B Nikpour, D Sinodinos, N Armanfard
IEEE Trans. on Neural Networks and Learning Systems (IEEE TNNLS 2024)
.png)
This paper aims to review the current approaches in self-supervised anomaly detection, present their technical details, and discuss their strengths and drawbacks.
H Hojjati, TKK Ho, N Armanfard
Neural Networks (Elsevier 2024)

This paper provides an artificial neural network methodology to predict lower yield strength (LYS) and ultimate tensile strength (UTS).
S Sinha, D Guye, X Ma, K Rehman, S Yue, N Armanfard
Machine Learning with Applications (Elsevier; 2024)

In this paper, we propose a method, DASVDD, that jointly learns the parameters of an autoencoder while minimizing the volume of an enclosing hyper-sphere on its latent representation.
H Hojjati, N Armanfard
IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering (IEEE TKDE 2023)

In this paper, we propose a novel contrastive clustering method, Cross-instance guided Contrastive Clustering (C3), that considers the cross-sample relationships to increase the number of positive pairs.
M Sadeghi, H Hojjati, N Armanfard
34th British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC 2023, Oral)

This paper presents a novel approach to vehicle failure prediction called mVSG-VFP, which employs self-supervised learning and graph-based techniques. The proposed method realizes the failure prediction task by exploring information hidden in the time-series data recorded through the sensors embedded in the vehicle.
H Hojjati, M Sadeghi, N Armanfard

In this paper, we propose a deep multi-representation learning (DML) framework for data clustering whereby each difficult-to-cluster data group is associated with its own distinct optimized latent space.
M Sadeghi, N Armanfard
IEEE Trans. on Neural Networks and Learning Systems (IEEE TNNLS 2023)

In this work, we hypothesize that selecting relevant joints prior to recognition can enhance the performance of the existing deep learning-based recognition models.
B Nikpour, N Armanfard
IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (IEEE TSMC 2023)

In this paper, we propose a novel framework for finding temporal and spatial attentions in a cooperative manner for activity recognition.
B Nikpour, N Armanfard

In this paper, we propose to detect seizure channels and clips in a self-supervised manner where no access to the seizure data is needed.
TKK Ho, N Armanfard
Thirty-Seventh AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-2023, Oral)

We propose the Attentive Task Interaction Network (ATI-Net). ATI-Net employs knowledge distillation of the latent features for each task, then combines the feature maps to provide improved contextualized information to the decoder.
D Sinodinos, N Armanfard
26th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR 2022)

For the first time, we propose a contrastive learning-based framework that is suitable for acoustic anomaly detection.
H Hojjati, N Armanfard
IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP 2022, Oral)

In this paper, we propose a machine learning based framework to establish a model that accurately predicts roll forces at each mill stand of the hot strip rolling mill. The proposed model includes both steel chemistry and physical process parameters for its predictions.
S Shen, D Guye, X Ma, S Yue, N Armanfard
Machine Learning with Applications, Volume 7 (MLwA 2022)

We propose a deep clustering technique called IDECF, whereby the true cluster assignments are estimated using an individual deep fully connected network (FCM-Net), which takes its input from the latent space of an autoencoder.
M Sadeghi, N Armanfard
IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP 2021)

We propose to formulate the joint selection problem as a Markov Decision Process (MDP), where we employ deep reinforcement learning to find the most informative joints per frame.
B Nikpour, N Armanfard
IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC 2021)

In this paper, we propose a novel AE-based clustering scheme, Deep Successive Subspace Learning (DSSL), which simultaneously minimizes weighted reconstruction and clustering losses of data points.
M Sadeghi, N Armanfard
International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN 2021)

In this paper, we present a multiview feature selection method that leverages the knowledge of all views and uses it to guide the feature selection process in an individual view.
M Komeili, N Armanfard, D Hatzinakos
IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (IEEE TPAMI 2020)

In this work, the differences in resting-state BCGs of the two cohorts in a sitting posture were quantified.
S Chang, S Mak, N Armanfard, J Boger, A Mihailidis
IEEE Journal of Translational Engineering in Health and Medicine (IEEE JTEHM 2020)

In this paper, we propose a practical machine learning (ML) based approach for the detection of MMN components, thus improving the accuracy of prediction of emergence from coma.
N Armanfard, M Komeili, J P Reilly, J F Connolly
IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics (IEEE JBHI 2019)

In this paper, a zero-effort device, a floor tile, was used to develop an unobtrusive BP monitoring technique.
S Chang, N Armanfard, A Q Javaid, J Boger, A Mihailidis
IEEE Journal of Translational Engineering in Health and Medicine (IEEE JTEHM 2018)

This paper proposes a novel algorithm for localized feature selection for which each region of the sample space is characterized by its individual distinct feature subset that may vary in size and membership.
N Armanfard, J P Reilly, M Komeili
IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems (IEEE TNLS 2018)

In this paper, we approach the biometric recognition problem from a different perspective by incorporating electrocardiogram (ECG). Compared with conventional biometrics, stealing someone’s ECG is far more difficult if not impossible.
M Komeili, N Armanfard, D Hatzinakos
IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics & Security (IEEE TIFS 2018)

This paper proposed a method that uses local information in terms of sample margins while enforcing an across-session measure. This makes it a perfect fit for biometric recognition problems.
M Komeili, W Louis, N Armanfard, D Hatzinakos
IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics (2018)

In this paper, we developed a novel home-based package that measures critically important physiological information such that neither active compliance nor interaction from the user is required.
N Armanfard, M Komeili, A Mihailidis
Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC)(2018)

In this paper, we propose a novel localized feature selection (LFS) approach whereby each region of the sample space is associated with its own distinct optimized feature set
N Armanfard, J P Reilly, M Komeili
IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (IEEE TPAMI 2016)

In this paper, we propose a practical machine-learning approach for the identification of vigilance lapses using EEG signals recorded from a very sparse electrode configuration with only 4 electrodes
N Armanfard, M Komeili, J P Reilly, L Pino
IEEE Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering (2016)

